In this article, we will discuss the importance of Internet Access and why it should be considered a basic human right.
With everything around us becoming digital, the internet has become an inseparable part of our routine. Aside from lightening our mood by serving us rich content through memes. It acts as the main source of information exchange and communication.
From healthcare, education, and effective business management to online retail, we now rely on the Internet. Given its importance today, life without it seems unimaginable for most of us.
Since the internet has embedded itself in our everyday life, many people consider denying access to the internet, as a breach of human rights.
What Is the Internet?
In formal terms, the Internet is a global system of numerous devices connected via computer networks. These networks use a uniform Internet protocol suite based on TCP/IP to transfer information between different devices
With the help of these networks, the Internet provides a wide variety of services. Such as the World Wide Web, interlinked hypertext documents, IP telephony, email communication, and file-sharing networks.
Restrictions on Internet Access across the World
Currently, more than 4.5 billion users are connected to the internet at any given time. Compared to 1995, when only 1% of the internet had regular access to the internet, the number has grown to 40% of the world population.
Despite the billions of people using the Internet worldwide, several pockets of the population lack access to it. In total, 60% of the population lacks regular internet access, with the least developed nations providing internet access only to 10% of their population.
Many of these regions that lack access to the Internet are developing countries. However several countries also restrict or control the content shared on websites in their country, on purpose.
This is why the United Nations discredits the lack of access and suppressive tactics by certain governments, declaring “online freedom” a human right. In July 2016, the United Nations presented a resolution for a human rights-based approach to make the Internet open and expand its access to more users.
However, despite massive support for recognizing access to the internet as a human right. Many developed nations have not followed suit. Several countries such as Russia, China and South Africa rejected this resolution.
Why Is the Internet Such an Important Part of Our Lives?
Although the popularity of the Internet as a social network began in 1989, its origins can be traced back to the 1960s. Since the internet was established as a web. Its usage has increased exponentially with as many as 31 billion devices being a part of the internet.
One of the reasons the platform became so popular was that it provided users with unlimited access to information and communication. It helped people connect with each other and shaped the modern age.
First, businesses and organizations use it as an inexpensive means to reach their target audience. Technologies such as cloud computing, flourished because of the internet. It enabled businesses to provide high-performing applications and services conveniently and in a scalable manner.
With the advent of social media, more people started to connect using channels like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter. Social media developed awareness regarding many social issues in public and helped nations build people-to-people connections.
The Role of STUN Protocols in VoIP Implementation
Likewise, the entertainment industry prospered solely because it got more coverage than before. Fans could know when their favourite game or movie is releasing, attend events, and even talk to celebrities themselves.
The internet allowed people to attend lectures remotely and gain knowledge that wasn’t accessible to them before. It facilitated an era of online learning where people could seek education without ever having to leave their homeland.
However, the biggest impact of the internet was on online retail. Businesses and consumers were able to buy and sell products independently without restrictions in a free market, helping it reach the size of 4,206 billion dollars in 2020.
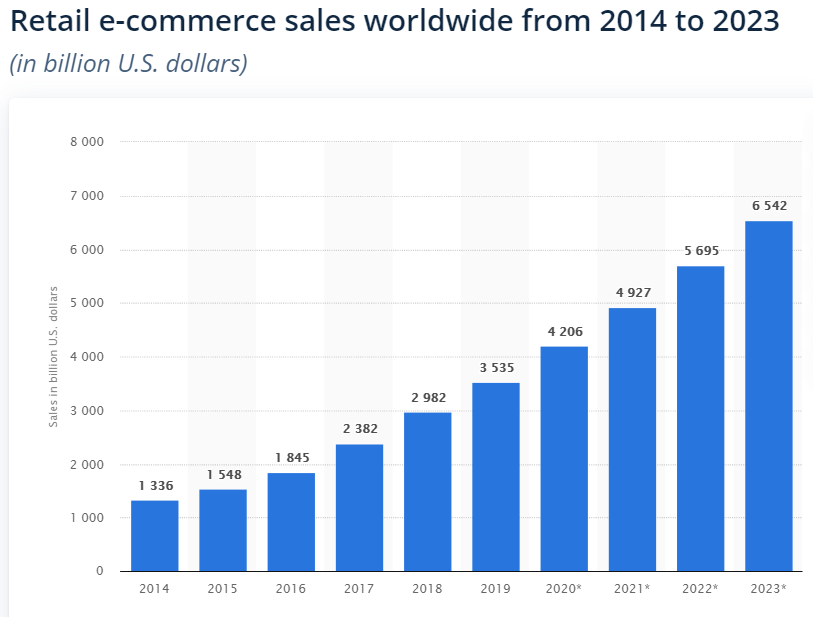
1 Based on previous data, global e-commerce is expected to be worth $6,542 billion by 2023.
To this day, the Internet plays a crucial role in a variety of different sectors such as education, banking, medicine, etc. Especially, with social distancing in place, its availability has become even more necessary to local communities.
From the onset of 2020, the use of the internet has increased by as much as 70%, largely because people cannot leave their homes after the outbreak of Covid-19. The Internet is a source for accessing education, employment, and healthcare in many countries and regions.
The Internet gives both people and businesses tremendous earning potential and enhances their quality of living and operations. Having access to fast and reliable internet means that people can continue with their education even when they are immobilized in their homes.
All the while, it provides access to remote diagnosis, remote work as well as maintaining social relationships personal and professional relationships. This is why, like education, employment, and healthcare, the internet, too, has to be regarded as a basic human right.
The Internet as a Human Right
Although many corporations and countries consider broadband as just another exploitable resource, experts consider it to as an essential tool for building a healthy democracy and maintaining freedom of expression.
This is why people consider access to the internet as a basic human right, arguing that it needs to be provided for free, especially to those who can’t afford it. Various studies have found that the Internet is essential for keeping people in power accountable.
Quoting Dr. MertenReglitz, who was behind this study:
“Internet access is not merely a luxury for those who can afford it. It is instead highly conducive to a multitude of crucial human interests and rights. Internet access is a uniquely effective way for lobbying and holding accountable global players like global governance institutions and multinational corporations.”
Reglitz points out that gender inequality also plays a role in blocking access to the internet for some people. A World Wide Web Foundation study discovered that globally men were 33% more likely to have access to the internet than women.
Although the lack of access to the internet is a global problem, it surprisingly exists in the largest economy of the world. The United States. Currently, millions of Americans lack access to high-speed internet, with millions more not being able to use the internet at all. Research by Pew highlighted that as many as 33 million US citizens don’t use the internet.
Read Also: TCP vs UDP – Which Solution Is Optimized for VoIP Solutions
On the other hand, the federal government believes that approximately 25 million Americans lack access to broadband speed. However, Microsoft clarifies that these numbers are misleading and that as many as 162.8 million cannot access the internet at broadband speeds.
Considering that basic needs such as healthcare, education, and employment, as well as liberties like a democratic process, are tied to the internet. Making internet access a human right is essential for the collective growth of our global community.
However free access to the internet will not solve all the problems people face. It will pave the way for making people more informed and uplifting them both socially and economically.